In an increasingly digital world, the protection of personal information has never been more critical. This is especially true in healthcare, where sensitive patient data is handled daily. The Caldicott Principles provide a framework for ensuring that personal information is used appropriately and kept secure. In this article, we’ll explore what the Caldicott Principles are, why they matter, and how they are applied in healthcare settings.
What Are the Caldicott Principles?
The Caldicott Principles were first introduced in 1997 in the UK, following a review led by Dame Fiona Caldicott. The purpose of the review was to ensure that patient information was being shared and handled appropriately, particularly with the rise of electronic patient records. The principles provide a set of guidelines to help healthcare organizations balance the need to share patient information with the necessity to protect patient confidentiality.
The Seven Caldicott Principles
Let’s dive into each of the seven Caldicott Principles to understand their importance and application in healthcare.
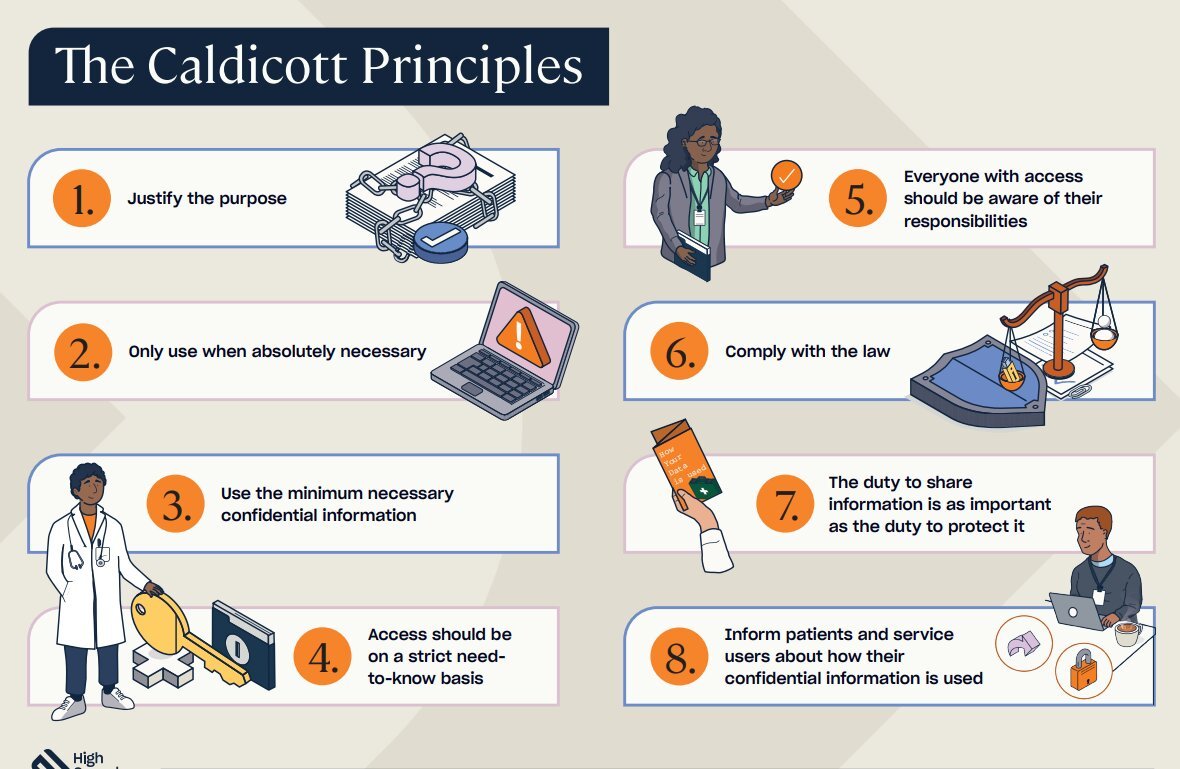
1. Justify the Purpose
The first principle states that every proposed use or transfer of patient-identifiable information within or from an organization should be clearly defined, scrutinized, and justified. This means that healthcare professionals must ensure that there is a legitimate reason for accessing or sharing patient data.
Why It Matters: This principle ensures that patient information is only used when absolutely necessary, reducing the risk of unnecessary or inappropriate access.
2. Don’t Use Personal Confidential Data Unless Absolutely Necessary
This principle emphasizes the importance of using the minimum amount of personal information required to achieve the intended purpose. If it is possible to complete a task without using patient-identifiable information, then this should be done.
Why It Matters: By limiting the use of personal data, this principle minimizes the potential for breaches of confidentiality and respects patient privacy.
3. Use the Minimum Necessary Personal Confidential Data
Building on the second principle, this one specifies that only the minimum amount of patient-identifiable information should be used. For example, if only the patient’s date of birth is needed to complete a task, there’s no need to access their full medical history.
Why It Matters: This principle helps to protect patient information by ensuring that only essential data is used, thereby reducing the exposure of sensitive information.
4. Access to Personal Confidential Data Should Be on a Need-to-Know Basis
This principle dictates that access to patient information should be restricted to those individuals who need it to perform their duties. Not everyone in a healthcare organization should have access to all patient data.
Why It Matters: Restricting access helps to safeguard patient information, ensuring that it is only seen by those who need it to provide care or perform essential tasks.
5. Everyone with Access to Personal Confidential Data Should Be Aware of Their Responsibilities
All staff members who handle patient information must understand their responsibilities under the Caldicott Principles. This includes knowing how to handle data securely and understanding the importance of confidentiality.
Why It Matters: Ensuring that all staff are aware of their responsibilities helps to create a culture of confidentiality and security within healthcare organizations.
6. Comply with the Law
Patient information must be handled in compliance with the law. This includes following relevant data protection legislation and ensuring that any data sharing is legal and justified.
Why It Matters: Compliance with the law is essential to protect patient rights and avoid legal consequences for healthcare organizations.
7. The Duty to Share Information Can Be as Important as the Duty to Protect Patient Confidentiality
This final principle recognizes that while protecting patient information is critical, there are times when sharing information is necessary for patient care. For example, sharing information between different healthcare providers can be essential for ensuring continuity of care.
Why It Matters: This principle ensures that patient care is not compromised by an overzealous focus on confidentiality, balancing the need to share information with the need to protect it.
The Role of the Caldicott Guardian
In addition to the principles themselves, the concept of a Caldicott Guardian was introduced. A Caldicott Guardian is a senior person within a healthcare organization responsible for overseeing the implementation of the Caldicott Principles. They act as a gatekeeper, ensuring that patient information is handled appropriately and that any data-sharing decisions are made with patient confidentiality in mind.
Responsibilities of a Caldicott Guardian:
- Ensuring that the organization’s practices align with the Caldicott Principles.
- Providing advice on the use of patient information.
- Ensuring staff are trained and aware of their responsibilities regarding patient confidentiality.
- Reviewing and approving data-sharing arrangements.
Applying the Caldicott Principles in Practice

To effectively implement the Caldicott Principles, healthcare organizations must take a proactive approach. Here are some practical steps that can be taken:
1. Regular Training and Awareness Programs
Staff should receive regular training on the Caldicott Principles and the importance of patient confidentiality. This helps to ensure that everyone in the organization understands their responsibilities and knows how to handle patient data securely.
2. Data Minimization Strategies
Organizations should adopt data minimization strategies to ensure that only the minimum necessary patient information is used. This might include anonymizing data where possible or restricting access to only those who need it.
3. Robust Access Controls
Access to patient information should be tightly controlled. This might involve using role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
4. Regular Audits and Reviews
Regular audits and reviews of data handling practices can help to identify any potential issues and ensure that the Caldicott Principles are being adhered to. This might include reviewing access logs, data-sharing agreements, and staff training records.
5. Clear Data Sharing Policies
Organizations should have clear policies in place for data sharing, ensuring that any sharing of patient information is justified, legal, and in line with the Caldicott Principles. This might involve having formal data-sharing agreements in place with other healthcare providers.
The Impact of the Caldicott Principles on Patient Trust
The Caldicott Principles play a crucial role in maintaining patient trust in the healthcare system. When patients know that their information is being handled with care and only shared when necessary, they are more likely to be open and honest with their healthcare providers. This, in turn, can lead to better patient outcomes, as healthcare providers have access to accurate and complete information.
Challenges in Implementing the Caldicott Principles
While the Caldicott Principles provide a valuable framework for protecting patient information, implementing them can be challenging. Some of the key challenges include:
1. Balancing Confidentiality with Care Needs
Sometimes, the need to protect patient information can conflict with the need to share it for care purposes. Striking the right balance between these competing demands can be difficult.
2. Keeping Up with Technological Advances
As technology evolves, so too do the ways in which patient information can be accessed, shared, and stored. Healthcare organizations must continually adapt to these changes to ensure that they continue to comply with the Caldicott Principles.
3. Ensuring Consistency Across Organizations
Ensuring that the Caldicott Principles are applied consistently across different organizations and sectors can be challenging. This is particularly true in cases where patient information is shared between different healthcare providers.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of the Caldicott Principles
The Caldicott Principles remain as relevant today as they were when they were first introduced. As healthcare continues to evolve, with more data being collected and shared than ever before, these principles provide a vital framework for protecting patient confidentiality.
By adhering to the Caldicott Principles, healthcare organizations can ensure that patient information is handled with the utmost care and respect, maintaining trust and ensuring that patient care is not compromised. Whether you are a healthcare professional or a patient, understanding the importance of these principles is crucial in today’s data-driven world.
In summary, the Caldicott Principles serve as a cornerstone for patient data protection, ensuring that patient information is used appropriately and securely in healthcare settings. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, these principles will continue to play a vital role in safeguarding patient privacy.